life expectancy after leg amputation diabetes
Further adjustment for smoking blood pressure body mass index myocardial infarction or stroke did not change these results substantially Table 3. There are certain conditions that increase the chance an ulcer will develop as well as if it can be healed.
Diabetic Amputations A Shameful Metric Of Inadequate Care Kaiser Health News
If that isnt bad enough diabetics with amputations dont live very long.
. The NHS reports that people who have diabetes are 15 times more likely to undergo amputations than other people without the condition. In terms of age the greatest risk of postoperative death was observed among those 75 years of age. 65 of all of those with a diabetic amputation are dead 5 years.
Compared with patients 5064 years of age this group had a 59 greater risk of death after a major amputation 158 95 CI 115218 and four times the risk after a minor amputation 415 95 CI 245703. How long does diabetes live after leg amputation I PRESUME you are referring to DM - Diabetes Mellitus - as opposed to DI Diabetes Insipidus. 2 Among primary care patients with DM lower-limb amputations are required in approximately 1 to 7 3 and 20 to 50 risk losing the contralateral leg to.
During this time these patients have prolonged stays in healthcare settings and limited access to hospice services. Survival could be predicted by duration of insulin use age sex and renal insufficiency. We know that about 50 of all diabetics with an amputation are dead 3 years after the amputation.
I have known quite a few people with diabetes who have been able to get up and moving again safely and lived much longer than 5 years after their amputations. If that isnt bad enough diabetics with amputations dont live very long. Compared with 213 300 controls 3113 amputees were less likely to die at home 155 versus 249 per cent.
We know that about 50 of all diabetics with an amputation are dead 3 years after the amputation. There was no difference among patients. Answer 1 of 3.
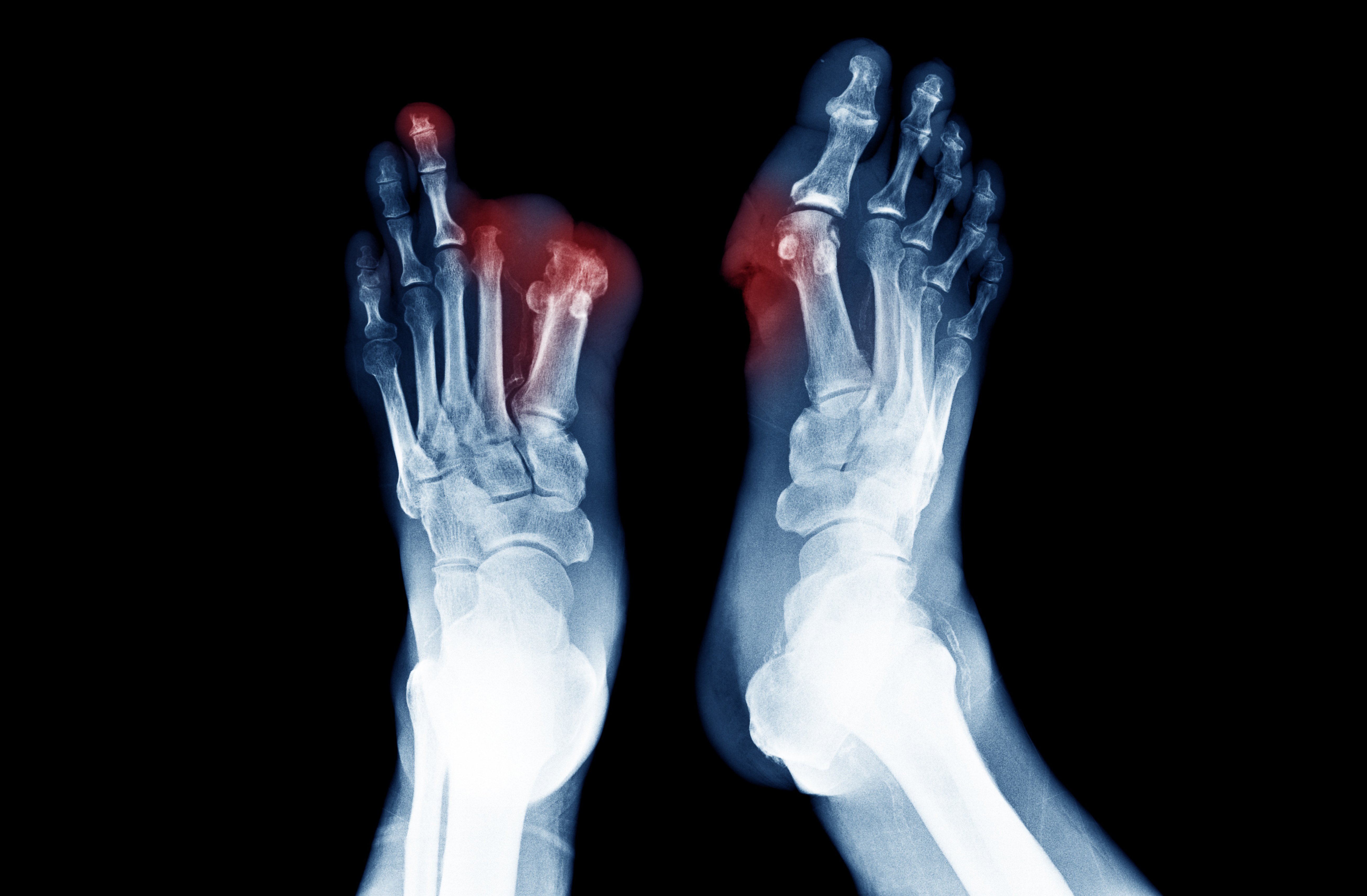
Ii These non-healing foot ulcers are caused by high blood glucose levels which accelerate the direct damage to the. Charity Diabetes UK notes that problems of the foot are the most frequent reasons for hospitalisation amongst patients. They observed that 1 of every 10 patients 11 who underwent a major amputation died within 30 days of their procedure and 1 in 6 18 died within 90 days.
Risk Factors for Diabetic Foot Ulcers. If that isnt bad enough diabetics with amputations dont live very long. 19 2019 in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology indicate unmet palliative care needs of.
Some that I know you cannot even tell that they have an artificial leg. 65 of all of those. Three years after the first diabetic amputation 483 will have another amputation.
Five-year mortality rates after new onset diabetic ulceration have been reported are between 43 and 55 percent and up to 74 percent for patients with lower-extremity amputation2 Ulceration is however a final result of many poor habits poor diabetes management and a lack of preventative action. Look past the statistics and find the hope. After a lower limb amputation someone with diabetes remains in the hospital an average of 9-12 days.
Won et al reported 1-year mortality rates of patient with diabetic foot ulcers who did and did not undergo amputation as 34 n 114 and 3 n 167 respectively6 Fortington et al determined life expectancy to be 25 months in patients who underwent lower extremity major amputations compared with 207 months in patients with non-diabetic vascular. Within 5 years of a diabetes related amputation 607 will have another amputation. We know that about 50 of all diabetics with an amputation are dead 3 years after the amputation.
Cases Where Non-Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Occur. Of the seven diseases. 65 of all of those with a diabetic amputation are dead 5 years.
In conclusion this study highlighted high re-intervention re-amputation and new ulceration rates. Although this rate of postoperative. Diabetes is one of the leading causes of amputation of the lower limbs throughout the world.
At 12 months 802 of study cohort had a completely healed amputation site. Amputation increased mortality risk more than 4-fold in patients without diabetes HR 46 95 CI 2876 as well as in patients with diabetes HR 46 95 CI 3364. Amputees also had higher end-of-life healthcare costs across all sectors.
Every year surgeons perform a lower-limb amputation due to diabetes on about 73000 patients. From research life expectancy after amputation is a serious picture with a bleak outlook. In 124 of participants the amputation site remained incompletely healed.
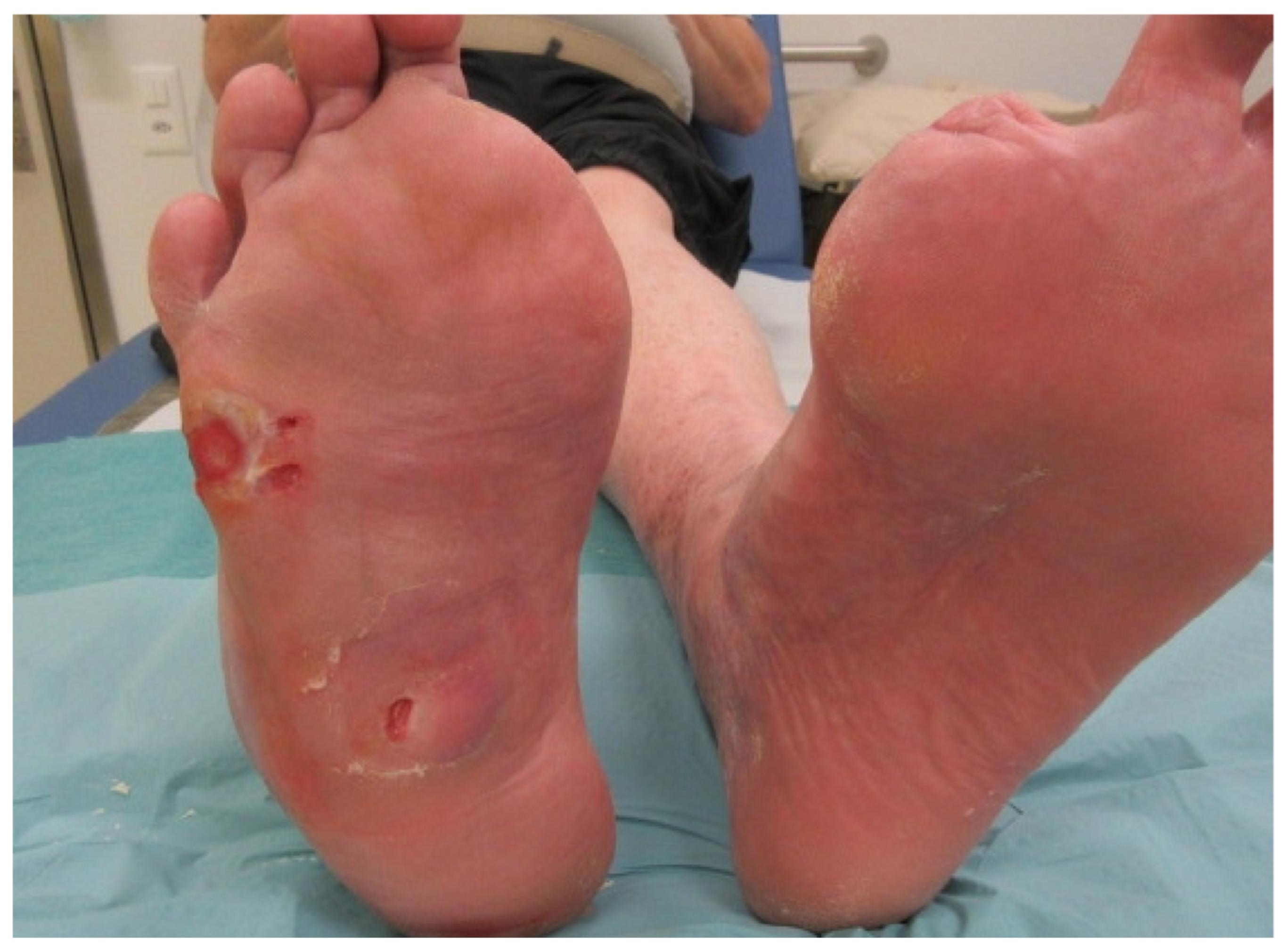
Diabetic foot ulcers are preventable. A consecutive series of 93 amputations 16 toefoot 33 trans-tibial 9 through knee and 42 trans-femoral were studied. Unfortunately there is only a 2- to 5-year life expectancy following amputation for chronic vascular disease for 60 of patients because of the risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
This figure was significantly higher than those reported by previous studies on life expectancy following lower limb amputation due to diabetes which ranged between 3 and 5 percent. The mortality 1 3 and 5 years after the index amputation was 15 38 and 68 respectively and was higher in patients who had achieved healing after major amputation than in patients achieving healing after minor amputation. Their mean age was 758 years.
P 0001 and spent a greater number of their last 90 days of life in hospital median 19 versus 8 days. Only 209 had no complications in 12 months. The findings published Feb.
21 23 were admitted from a nursing home and 87 92 were amputated due to a vascular disease andor diabetes. Life expectancy is low 3 years in DM patients requiring below-knee amputations for untreatable foot problems. Thirty days and 1-year mortality were 30 and 54 respectively.
Death was less frequent among those who underwent a minor amputation but not insubstantially with 3 having died within 30 days and 6 within 90 days. There are three types of the former and four types of the latter -and all seven types have sub-types. Strategies to improves these outcomes in.
Nearly one in 10 patients with end-stage kidney failure undergoes toe foot or leg amputation in their last year of life. The research team also found that individuals who were younger than 65 when their leg was amputated lived longer than older amputees. The rate of new amputations after 1 3 and 5 years of observation was 14 30 and 49 respectively.
I Most of these amputations are performed for the treatment of non-healing diabetic foot ulcers that resulted from peripheral arterial disease PAD.

25 Must Know Statistics About Amputation Due To Diabetes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diabetic-foot-ulcers-and-sores-5210539-v1-17fa850b86534b03b1b6cdc6db8bf54f.jpg)
Diabetic Sores And Foot Ulcers Causes Treatment Prevention
Medicina Free Full Text Treating Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis A Practical State Of The Art Update Html

Pin By Deeksha On Diabetes Nutrition Diabetes Diabetic Diet Diabetes

End Of Life Care Is Aggressive For Amputees On Dialysis Newsroom
Limb Amputation News Mesi Simplifying Diagnostics

What Happens When The Limb Is Gone But The Pain Remains
How Diabetes Can Increase The Risk Of Limb Amputation
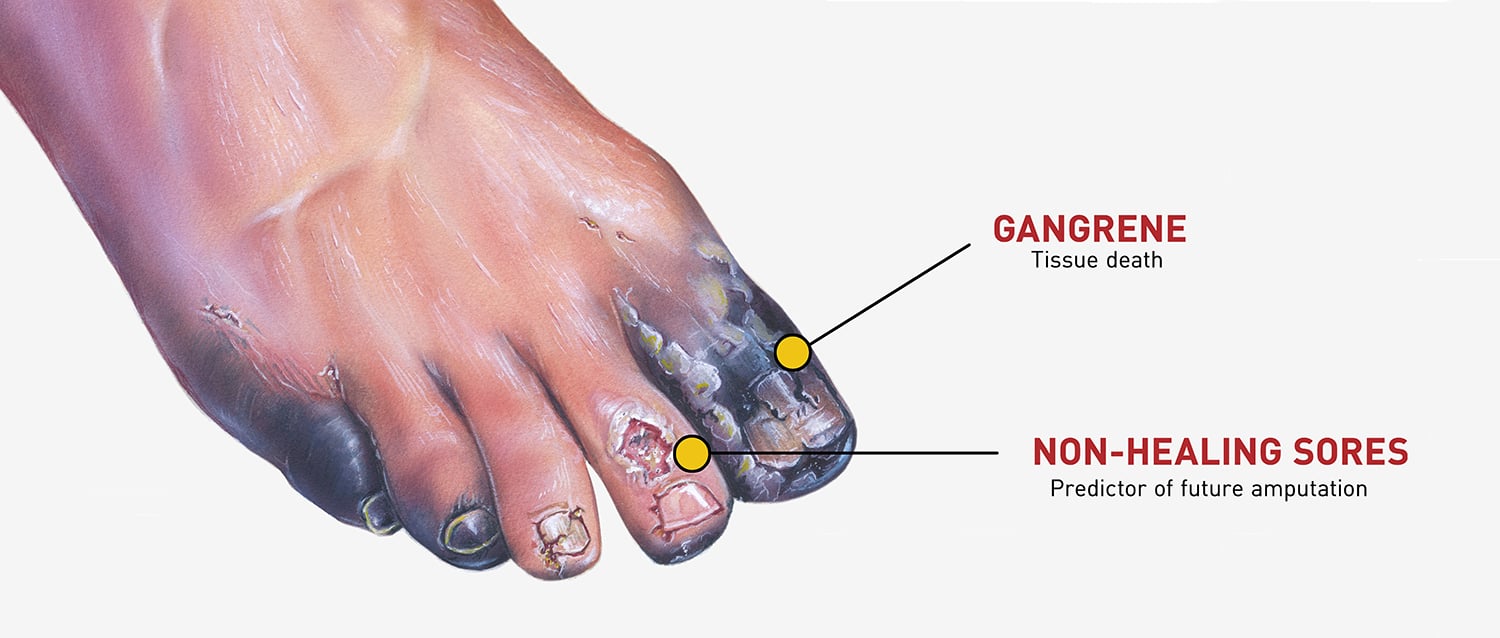
Diabetes And Amputation A Matter Of Life And Limb

Peripheral Artery Disease Pad Modern Vascular Peripheral Artery Disease Vascular Arteries

Diabetic Dermopathy Causes Symptoms Treatments And Pictures

Rise In Diabetes Related Lower Limb Amputations
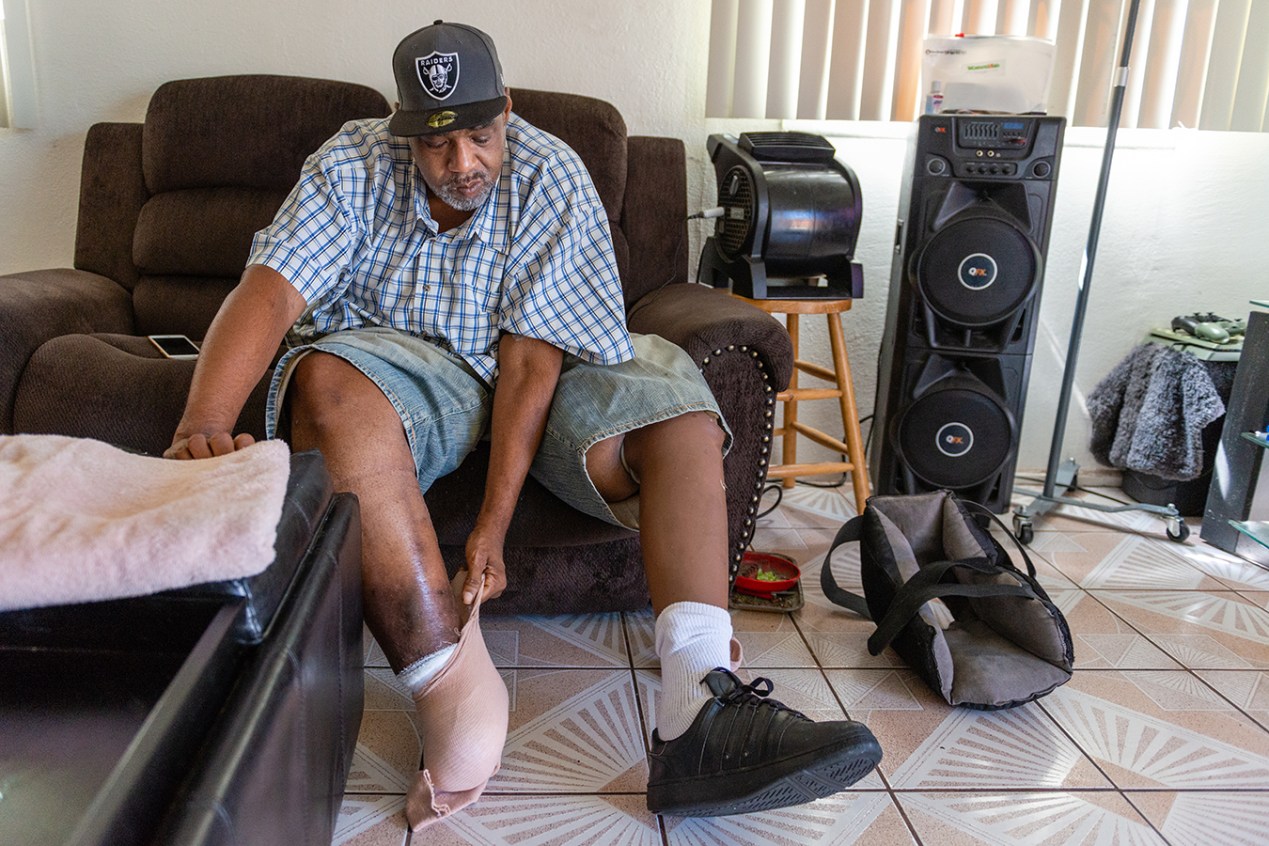

Diabetic Amputations A Shameful Metric Of Inadequate Care Kaiser Health News

Diabetes And Amputation A Matter Of Life And Limb

Diabetic Foot Problems Symptoms Treatment And Foot Care

Diabetes And Amputation Save Your Limb Before It S Too Late Goke Akinwande Md Vascular And Interventional Radiologist

Amputations Not Always Necessary For Patients With Diabetes And Gangrene Malmo University

